EXPLORER
THE ALPHABET
PRACTICA TU DESTREZA AUDITIVA

Study 15 minutes every day.
Listen to songs
Watch series or cartoons in english
Practice what we have learnt in class.
WATCH PEPPA PIG TO IMPROVE YOUR ENGLISH
Sing the song with me!
| SONG IN ENGLISH If you're happy and you know it Clap your hands (Clap, Clap) If you're happy and you know it, Clap your hands (Clap, Clap) If you're happy and you know it, And you really want to show it*, If you're happy and you know it, Clap your hands (Clap, Clap). If you're happy and you know it Stomp your feet (Stomp, Stomp) If you're happy and you know it, Stomp your feet (Stomp, Stomp) If you're happy and you know it, And you really want to show it, If you're happy and you know it, Stomp your feet (Stomp, Stomp) If you're happy and you know it Shout "hurray"! (Hur-ray!) If you're happy and you know it, Shout "hurray"! (Hur-ray!) If you're happy and you know it, And you really want to show it, If you're happy and you know it, Shout "hurray"! (Hur-ray!) If you're happy and you know it, Do all three (Clap, Clap, Stomp, Stomp, "Hur-ray!") If you're happy and you know it, Do all three (Clap, Clap, Stomp, Stomp, "Hur-ray!") If you're happy and you know it, And you really want to show it, If you're happy and you know it, Do all three (Clap, Clap, Stomp, Stomp, "Hur-ray!") |
SONG IN SPANISH Si eres feliz y lo sabes Bate las manos (clap, clap) Si eres feliz y lo sabes Bate las manos (clap, clap) Si eres feliz y lo sabes Entonces pon las señales Si eres feliz y lo sabes Bate las manos (clap, clap) Si eres feliz y lo sabes Dé patadas (pum pum) Si eres feliz y lo sabes Dé patadas (pum pum) Si eres feliz y lo sabes Entonces pon las señales Si eres feliz y lo sabes Dé patadas (pum pum) Si eres feliz y lo sabes Grita hurra (¡Hu-rra!) Si eres feliz y lo sabes Grita hurra (¡Hu-rra!) Si eres feliz y lo sabes Entonces pon las señales Si eres feliz y lo sabes Grita hurra (¡Hu-rra!) Si eres feliz y lo sabes Haz los tres (clap, clap, pum pum, "¡Hu-rra!") Si eres feliz y lo sabes Haz los tres (clap, clap, pum pum, "¡Hu-rra!") Si eres feliz y lo sabes Entonces pon las señales Si eres feliz y lo sabes Haz los tres (clap, clap, pum pum, "¡Hu- |
| Pronombres personales | --------- |
|
| Determinantes posesivos | |
| my - mi your - tu his - su (para él) her - su (para ella) its - su (para objetos, animales...) our - nuestro your - vuestro their - su (para ellos o ellas) |
| Verbo to be (Afirmativo) | |
| I am - yo soy o estoy you are - tú eres o estás he is - él es o está he is - ella es o está it is - el/ella es o está (animales, cosas...) we are - nosotros/as somos o estamos you are - vosotros/as sois o estáis they are - ellos/as son o están Interrogativo cambia el orden . Am I?, Are you?, Is he?, Is she?, Is it? Are we?, Are you?, Are they? Negativo añade not al final contraido o sin contraer: I am not, You are not (You aren't) He is not (He isn't), She is not(She isn't), It is not (It isn't), We are not (We aren't), They are not (They aren't) PRACTICE |
| Verbo have got | o | ||||
| I have got - yo tengo you have got - tú tienes he has got - él tiene she has got - ella tiene it has got - él/ella tiene (animales, objetos...) we have got - nosotros/as tenemos you have got - vosotros/as tenéis they have got - ellos/as tienen Interrogativo cambia el orden: Have you got?Negativo añade not : I haven't got Determinantes: this (esto/e/a),
that ( aquello/aquel/aquella/eso/ese/esa/)
these (estos/as)
those (esos/as/aquellos/as)
Pronombres interrogativos:
Days of the week: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday. Months: January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, December. Ordinals numbers: first, second, third, fourth, fifth, sixth, seventh, eighth, nineth, tenth, eleventh, twelveth... |
UNIT 1. IN THE TREES
VOCABULARY :
ACTIONS: Listen to an MP3 player, laugh, eat popcorn, sleep,
write a note, read a magazine, shout, draw.
Wear, dance, sad, scarf, sing, jacket, hat, take
photos, climb, angry, run, happy, cold, gloves, walk, guitar,
car, What’s Bernard doing? He isn’t (eating popcorn). He’s
(making a new car).
FEELINGS: scared, tired, hungry, thirsty, excited, Is Becca (tired)?
Yes, she is. / No, she isn’t. Are Alfie and Josh (scared)? Yes, they
are. / No, they aren’t.
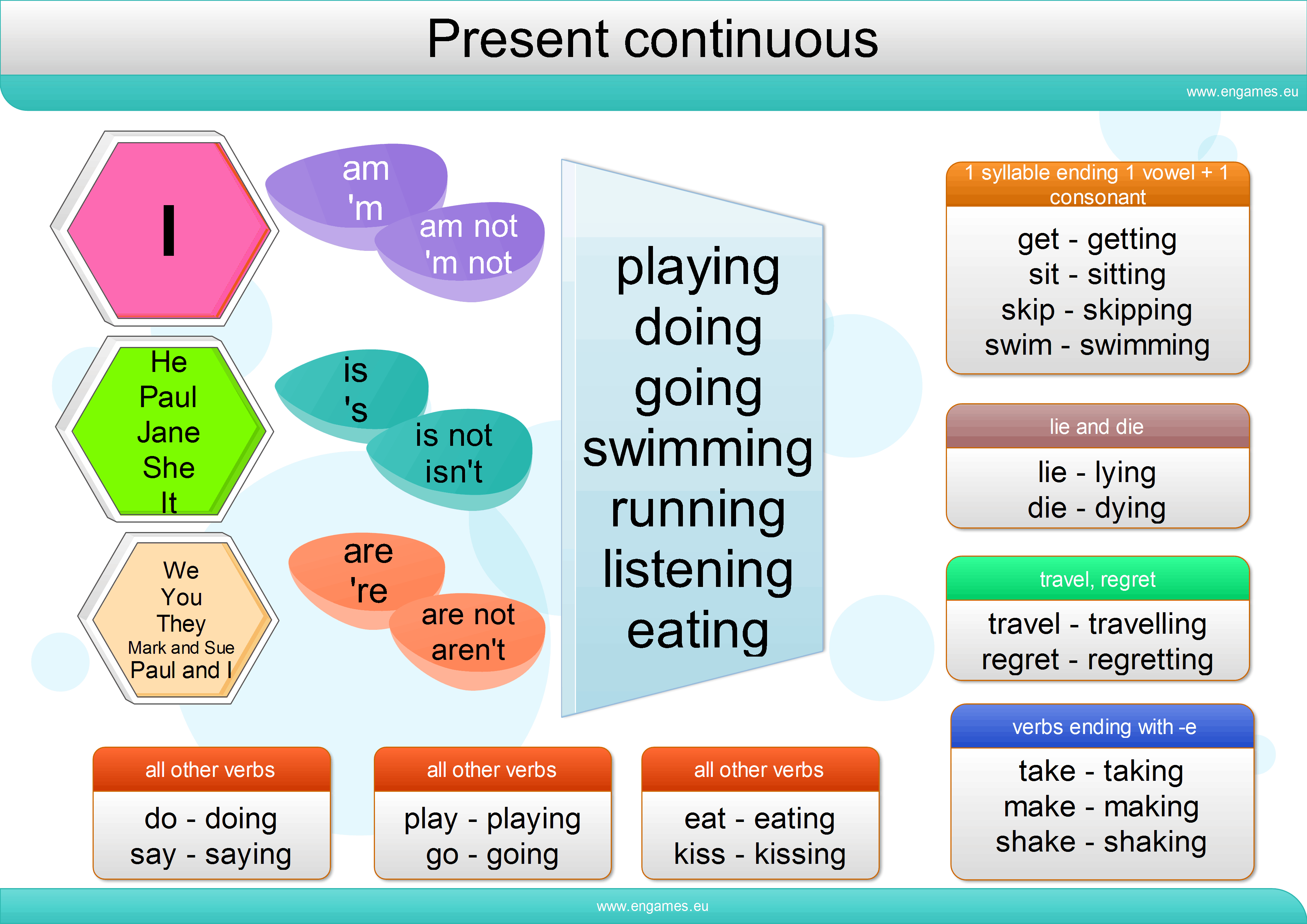
GRAMMAR : PRESENT CONTINUOUS
UNIT 1. IN THE TREES
VOCABULARY :
ACTIONS: Listen to an MP3 player, laugh, eat popcorn, sleep, write a note, read a magazine, shout, draw.
ACTIONS: Listen to an MP3 player, laugh, eat popcorn, sleep, write a note, read a magazine, shout, draw.
Wear, dance, sad, scarf, sing, jacket, hat, take
photos, climb, angry, run, happy, cold, gloves, walk, guitar,
car, What’s Bernard doing? He isn’t (eating popcorn). He’s
(making a new car).
FEELINGS: scared, tired, hungry, thirsty, excited, Is Becca (tired)? Yes, she is. / No, she isn’t. Are Alfie and Josh (scared)? Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
GRAMMAR : PRESENT CONTINUOUS
PRESENT CONTINUOUS(Se usa para expresar lo que estamos haciendo justo en el momento actual)
Verb To Be + V-ing
ESTRUCTURA - SUJ (I, YOU, WE, THEY)
I AM V-ing XX ESTRUCTURA - SUJ (HE, SHE, IT) YOU ARE V-ing
YOU AREN'T V-ing
ARE YOU V-ing?
Resp. af.: —YES, I AM.
Resp. neg.: —NO, I'M NOT.
WE ARE V-ing
THEY ARE V-ing
HE/SHE/IT IS V-ing
HE/SHE/IT ISN'T V-ing
IS HE/SHE/IT V-ing?
Resp. af.: —YES, HE IS.
Resp. neg.: —NO, HE ISN'T.
WHAT ARE YOU DOING?
WHAT IS HE DOING?
Examples
Examples I am taking photos in the countryside.
You aren't eating a sandwich.
Are you playing to the park? —Yes, I am.
We are acting at the theatre.
Are they listening to the CD player? —No, they aren't.
He is doing his homework.
She isn't swimming in the beach.
Is he studing in his bedroom? —Yes, he is.
Is she singing in the party? —No, she isn't.
PRESENT CONTINUOUS(Se usa para expresar lo que estamos haciendo justo en el momento actual)
Verb To Be + V-ing
Verb To Be + V-ing
| ESTRUCTURA - SUJ (I, YOU, WE, THEY) I AM V-ing | XX | ESTRUCTURA - SUJ (HE, SHE, IT) |
| YOU ARE V-ing YOU AREN'T V-ing ARE YOU V-ing? Resp. af.: —YES, I AM. Resp. neg.: —NO, I'M NOT. WE ARE V-ing THEY ARE V-ing | HE/SHE/IT IS V-ing HE/SHE/IT ISN'T V-ing IS HE/SHE/IT V-ing? Resp. af.: —YES, HE IS. Resp. neg.: —NO, HE ISN'T. | |
| WHAT ARE YOU DOING? | WHAT IS HE DOING? | |
| Examples | Examples | |
| I am taking photos in the countryside. You aren't eating a sandwich. Are you playing to the park? —Yes, I am. We are acting at the theatre. Are they listening to the CD player? —No, they aren't. | He is doing his homework. She isn't swimming in the beach. Is he studing in his bedroom? —Yes, he is. Is she singing in the party? —No, she isn't. |
INTERACTIVE BOOK ( PRESENT CONTINUOUS)
VÍDEO ( WHAT ARE YOU DOING?)
Structures
Present Simple+ time.
Affirmative - Interrogative
What time do you go to school?( ¿A qué hora vas al cole?)
I go to school at nine o'clock.(Voy al cole a las nueve en punto)
What time does he make his bed?(¿A qué hora hace él su cama?)
He makes his bed at half past eight.(Èl hace su cama a las ocho y media)
Negative
I don't wash the dishes at quarter past seven.(Yo no friego los platos a las siete y cuarto)
She doesn't feed the dog at quarter to six (Ella no le pone la comida al perro a las seis menos cuarto)
Grammar
Hi everybody! I'm The Present Simple Girl. I like habits and routines. I always do the same things and at the same time. For example, I always drink two glasses of milk in the morning and I usually arrive at school at twenty five past eight . I often wear jeans and T-shirts. I love pop music. I also love animals and plants. I havea beautiful garden.
I live with my parents and my brother, 
The Present Continuous Guy. He is very different from me. He never arrives on time for lunch. He likes new clothes and fashion, and he doesn't listen to pop music. He plays hard rock in a group called "Metal Bananas" . We are in an English club called The HappyVerby Gang. We go to the club on Saturdays.
Si quieres aprender cómo se forma y cuándo se usa el Present Simple haz click en los siguientes apartados:
Practica lo aprendido con los siguientes ejercicios:
"Let's practise"
Form Use Contrast  Exercise 1
Exercise 1 Exercise 2
Exercise 2 Exercise 3
Exercise 3  Exercise 4
Exercise 4  Exercise 1
Exercise 1
 Exercise 2
Exercise 2
 Exercise 1
Exercise 1
 Exercise 2
Exercise 2
Short answers: Yes, I do / No, I don't
Grammar
Hi everybody! I'm The Present Simple Girl. I like habits and routines. I always do the same things and at the same time. For example, I always drink two glasses of milk in the morning and I usually arrive at school at twenty five past eight . I often wear jeans and T-shirts. I love pop music. I also love animals and plants. I havea beautiful garden.
I live with my parents and my brother, 

The Present Continuous Guy. He is very different from me. He never arrives on time for lunch. He likes new clothes and fashion, and he doesn't listen to pop music. He plays hard rock in a group called "Metal Bananas" . We are in an English club called The HappyVerby Gang. We go to the club on Saturdays.
Si quieres aprender cómo se forma y cuándo se usa el Present Simple haz click en los siguientes apartados:
Practica lo aprendido con los siguientes ejercicios:
"Let's practise"
"Let's practise"
| Form | Use | Contrast |
Short answers: Yes, I do / No, I don't
Reinforce Activities
- Habits & Routines. By Isabel Pérez.
TIME
Para preguntar a qué hora se hace algo habitualmente se añade What timedelante de Do o Does, para responder se empieza con At. Si lo que me pregunta es qué hora es en este momente se empieza con It is.
- Habits & Routines. By Isabel Pérez.
Para preguntar a qué hora se hace algo habitualmente se añade What timedelante de Do o Does, para responder se empieza con At. Si lo que me pregunta es qué hora es en este momente se empieza con It is.
What time do you do your homework? At five o'clock.
What time is it? It is half past four.
Present simple Se usa para expresar nuestras rutinas diarias.
Forma afirmativa.
Se forma con el pronombre + el verbo (I read: Yo leo), la forma verbal nunca cambia, excepto en la 3º persona del singular (He, She, It).
Ésto suele suponer una dificultad, hay que acordarse de añadir una s (She reads: Elle lee).
A veces en vez de añadir s , se añade:
- es (wash - washes), cuando el verbo termina en sh.
- es (go - goes), también se añade cuando termina en o.
- ies (study - studies), cuando el verbo termina en y precedida de consonante.
Cuando el verbo es compuesto sólo se añade la s a la primera parte (gets up).
Para forma la forma interrogativa se añade delante del pronombre Do siempre, excepto para la 3º persona del singular (He,She It), que se le añade Does, y entonces no se le pone la s.
Do you read? : ¿Lees tú? Does he read? : ¿Lee él?
Para la forma negativa. se coloca Don't (contracción de Do not) entre el pronombre y el verbo. En la 3º persona del singular (He, She, It) se cambia por Doesn't (contracción de Does not) y tampoco se le pone la s. I don't read: Yo no leo. She doesn't read: Ella no lee.
It se usa para animales, objetos, para hablar del tiempo, de la hora o de cosas abstractas.
Se forma con el pronombre + el verbo (I read: Yo leo), la forma verbal nunca cambia, excepto en la 3º persona del singular (He, She, It).
Ésto suele suponer una dificultad, hay que acordarse de añadir una s (She reads: Elle lee).
A veces en vez de añadir s , se añade:
- es (wash - washes), cuando el verbo termina en sh.
- es (go - goes), también se añade cuando termina en o.
- ies (study - studies), cuando el verbo termina en y precedida de consonante.
Cuando el verbo es compuesto sólo se añade la s a la primera parte (gets up).
Para forma la forma interrogativa se añade delante del pronombre Do siempre, excepto para la 3º persona del singular (He,She It), que se le añade Does, y entonces no se le pone la s.
Do you read? : ¿Lees tú? Does he read? : ¿Lee él?
Para la forma negativa. se coloca Don't (contracción de Do not) entre el pronombre y el verbo. En la 3º persona del singular (He, She, It) se cambia por Doesn't (contracción de Does not) y tampoco se le pone la s. I don't read: Yo no leo. She doesn't read: Ella no lee.
It se usa para animales, objetos, para hablar del tiempo, de la hora o de cosas abstractas.
Reinforce Activities
Projects
Projects
- My Daily Routine. Descripción de la propia rutina diaria, de cada día de la semana.
- My friend. Escribir una entrevista al mejor amigo/a, con preguntas que incluyan cuál es su nombre, edad, dónde vive, cuántos hermanos y hermanas tiene, lo que le gusta (color, comida, asignatura), y lo que generalmente hace durante la semana.
Unit 3. COLLECTIONS
Structures
PRESENT SIMPLE
I collect I don´t collect Do I ....?
You collect You don´t collect Do you ......?
He collects He doesn´t collect Does he......?
She collects She doesn´t collect Does she .....?
It collects It doesn´t collect Does it .....?
We collect We don´t collect Do we......?
You collect You don´t collect Do you.....?
They collect They don´t collect Do they.....?
THERE IS ( SINGULAR ) /THERE ARE ( PLURAL )
There’s a (magnet ) on the fridge.
There isn’t a ( kitchen).
Is there a a mug ? Yes, there is. / No, there isn’t.
- My Daily Routine. Descripción de la propia rutina diaria, de cada día de la semana.
- My friend. Escribir una entrevista al mejor amigo/a, con preguntas que incluyan cuál es su nombre, edad, dónde vive, cuántos hermanos y hermanas tiene, lo que le gusta (color, comida, asignatura), y lo que generalmente hace durante la semana.
Unit 3. COLLECTIONS
Structures
PRESENT SIMPLE
I collect I don´t collect Do I ....?
You collect You don´t collect Do you ......?
He collects He doesn´t collect Does he......?
She collects She doesn´t collect Does she .....?
It collects It doesn´t collect Does it .....?
We collect We don´t collect Do we......?
You collect You don´t collect Do you.....?
They collect They don´t collect Do they.....?
THERE IS ( SINGULAR ) /THERE ARE ( PLURAL )
There’s a (magnet ) on the fridge.
There isn’t a ( kitchen).
Is there a a mug ? Yes, there is. / No, there isn’t.
Projects
Describe your house.
Going shopping
Mr Bean going shopping
Going shopping
Mr Bean going shopping
UNIT 4 ANIMALS
Structures:
Verb To Be: They are (Son) - They aren’t (No son) – Are they ? (¿Son?)
birds (aves), cats (felinos), carnivours, herbivours, omnivours, small (pequeños), big (grandes), medium (medianos), tall (altos), short (cortos, bajos), dangerous (peligrosos), wild (salvajes), domestic , funny (divertidos), in danger ( en peligro de extinción), mammal (mamíferos), fast (rápidos), slow (lentos), brown, black…
Verb Can : They can (Pueden) - They can’t (No pueden) – Can they? (¿Pueden?):
Run (correr), walk (andar), fly (volar), swim (nadar), climb (trepar), jump (saltar)…
Verb Have got: They have got (Tienen) - They haven’t got (No tienen) – Have they got? (¿Tienen?):
Big/small heads (cabezas grandes o pequeñas), ears (orejas ), long/short necks (cuellos cortos o largos), legs ( patas), tails ( colas), sharp teeth (dientes afilados), horns (cuernos), wings (alas), spots (manchas), stripes (rayas)…
Verb To live; They live (Viven) - They don`t live (No viven) – Do they live? (¿Viven?):
In water (en el agua), On land (en tierra), In the air (en el aire), in the jungle (en la selva), in the forest (en el bosque), in the savannah ( en la sabana), at the zoo (en el zoo)
Ver to eat: They eat (Comen) – Do they eat? (¿Comen?) – They don’t eat (No comen):
Leaves (hojas), grass (hierba), small animals (pequeños animals), meat (carne), plants , fruit, fish (pescado)…
GAME
PRONUNCIATION
EXERCISE
Write more descriptions about another animals: monkeys, giraffes, lions, snakes, zebras, crocodiles, elephants, …
Example: Monkeys.
They are brown, mammal and funny. They can jump and climb. They have got a small head, long arms and a long tail. They live on land and on trees. They eat bananas.
IN THE JUNGLE ( SONG )
Fill in the gaps
In the Jungle,
the mighty jungle,
the _____ sleeps tonight.
In the _____,
the quiet jungle,
the lions _____ tonight.
Near the village,
the peaceful ______,
the lions sleeps tonight.
_____ the village,
the quiet village,
the lions sleeps tonight.
Hush ____ darling,
don't fear my darling,
the lions sleeps ______.
Hush my darling,
don't ____ my darling,
the _____ _____ _____.
REINFORCE ( ANIMALS )
Animal body parts: spots, trunk, , wings, beak, tail, tongue, , horn, , feather, fur, stripes.
Habitat: Serengeti, forest, jungle, ocean, sea, river, lake, North Pole, savannah, pond, mountain. On land, in water, in air.
Diet: dead animals, plankton, grass, meat, leaves, fruit.
Abilities = can/can't: jump, eat, drink, walk, run, climb, swim, dive, talk, sing. LIVE.
Adjetives: dangerous, funny, fast, slow, very colourful.
Vocabulario pasivo:
ANIMALS DESCRIPTIONS
Para hacer descripciones, generalmente usamos el sujeto THEY, porque describimos cómo son los animales en general (lo hacemos en plural). También por esta razón no usarmos el artículo THE delante del nombre de los animales, porque hablamos en general (decimos HIPPOS, en lugar de *THE HIPPOS*).
Projects
AT THE ZOO. Proyecto de investigación sobre animales . Crear un álbum de recortes sobre los animales trabajados . Cada uno buscará imágenes relacionadas con su animal, y redactará un pequeño texto descriptivo: dónde viven, qué comen, de qué color son, si tienen pelo/plumas/piel, alas/patas/cola, y lo que puede o no pueden hacer (correr, volar, saltar, hablar, arrastrarse, andar...).
ONLINE:
Giant Pandas: Reading and Listening Comprehension. Un cuento popular sobre cómo los pandas adquieren su color y un interesante vídeo sobre pandas gigantes salvajes, para desarrollar destrezas de lectura y comprensión auditiva.
Koalas: No Tree .... No Me. Comprensión auditiva y lectura sobre koalas. Se puede usar con el imprimible ´Animals from Down Under" para practicar las cuatro destrezas.
The Mosquito: Listening and Reading Comprehension. Un interesante vídeo de National Geographic sobre el animal favorito de nadie, el mosquito, para practicar la comprensión auditiva, y un texto sobre cómo evitar los picotazos de mosquitos, para leer.
Vocabulary
PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE I
Revision
Shops
GIVING DIRECTIONS
Verb to be. Past tense
Verb To BE : Ser o estar
El verbo to be no necesita auxiliar. Para la interrogación cambia el orden y para la negación utiliza not.
Write the digital time.
Example:
12: 34 : It's twelve thirty four
PASADO - Simple Past
Cómo se forma el verbo en pasado
Estructura de la frase en pasado
En general, las oraciones en pasado tienen el mismo orden que las oraciones en presente:
Por tanto, lo único que varía es el AUXILIAR que se va a utilizar.
Auxiliares: DID - WAS / WERE -
ACTIVITIES TO REINFORCE VOCABULARY AND GRAMMAR
Subjects
English Inglés
Science / History Conocimiento del Medio
Maths Matemáticas
Art Plástica
Chinese Chino
Sport - Phisycal Educaction Deportes o Educación física
Music Música
Language Lengua
Religion Religión
Citizenship Ciudadanía
Places at School
Classroom Clase
Gym Gimnasio
Lab Laboratorio
Playground Recreo
Music classroom Clase de música
Canteen Comedor
Toilets Servicios
Hall Entrada
Assembly hall Salón de actos
Staffroom Sala de profesores
Office Despacho
Porch Porche
Track Pista
Schoolyard Patio
Ramp Rampa
Food
(repaso): ice cream, sandwiches, apples, cheese, salad, pizza, biscuits, cherries, chocolate, cake, fish, melon, bananas, pork, yoghourt, milkshake, orange juice, rice, chicken, watermelon, tomatoes, milk, chips, vegetables, soup...
Meals of the day
breakfast desayuno
lunch almuerzo
dinner cena
STRUCTURES:
Where do you / they have (English)? ¿Dónde tienes/tienen Inglés?
I/they have (English) in clasroom 5 Yo tengo/ellos tienen Inglés en la clase 5.
Where does he/she have (Sport)? ¿Dónde tiene él/ella deporte?
He/she has sport in the (gym). Él/ella tiene deporte en el gimnasio..
When do you/they have (Music)? I/they have music on (Mondays and Wednesdays). ¿Cuándo tienes/tienen música? Yo tengo/ellos tienen música los lunes y los míercoles
When does he/she have (Chinese)? He/she has (Chinese) on (Tuesdays and Thursdays). ¿Cuándo tiene él/ella chino? Él/ella tiene chino los martes y jueves.
What do you have for (breakfast)? ¿Qué tomas para desayunar?
I have (fruit) for breakfast. Yo tomo fruta para desayunar
What does he/she have for (lunch)? ¿Qué toma él/ella para almorzar?
He/she has (pasta) for (lunch). Él/ella toma pasta para almorzar
FOOD
DRINKS
VEGETABLES
FRUIT
BREAKFAST
JUNK FOOD
The very hungry caterpillar ( story )
Healthy food
Word - search
I..... wake up, get up, get dressed, have breakfast, wash my face, brush my teeth, comb my hair, make my bed, go to school ( by bus, on foot....)/ start school, go home/finish school, have lunch, do my homework, play ( computer, friends...), feed my pet, have a shower, have dinner, wash the dishes ( housework), watch television, read a book and go to bed.
TIME
Para preguntar a qué hora se hace algo habitualmente se añade What time delante de Do o Does, para responder se empieza con At. Si lo que me pregunta es qué hora es en este momente se empieza con It is.
HABITS AND ROUTINES
PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE
ACTIVITY TO REINFORCE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE 1º AND 3º PERSON
It's...
Reading
Read page 48 and aswer the questions.
Robert
1- How old is he?
2- Where does he live?
3- What's the weather like there?
4- What time does he get up?
5- What time does he do his homework?
6- What time does he go to bed?
Laura
7- How old is Laura?
8- Where does she live?
9- What's the weather like there?
10- What time does she get up in the week?
11- What time does she go to school?
12- What time does she have dinner?
REVIEW UNIT 5
DAILY ROUTINE
TO BE ( PAST TENSE)
PAST SIMPLE OF " TO BE "1
PAST SIMPLE OF " TO BE " 2
TO BE ( SIMPLE PRESENT/ SIMPLE PAST)
VOCABULARY( JOBS)
Fill in the gaps
In the Jungle,
the mighty jungle,
the _____ sleeps tonight.
In the _____,
the quiet jungle,
the lions _____ tonight.
Near the village,
the peaceful ______,
the lions sleeps tonight.
_____ the village,
the quiet village,
the lions sleeps tonight.
Hush ____ darling,
don't fear my darling,
the lions sleeps ______.
Hush my darling,
don't ____ my darling,
the _____ _____ _____.
REINFORCE ( ANIMALS )
Animal body parts: spots, trunk, , wings, beak, tail, tongue, , horn, , feather, fur, stripes.
- Partes del cuerpo comunes: head, ears, eyes, mouth, neck, legs. skin.
- Para completar la información: antlers, tentacles, antennae, shell.
Habitat: Serengeti, forest, jungle, ocean, sea, river, lake, North Pole, savannah, pond, mountain. On land, in water, in air.
Diet: dead animals, plankton, grass, meat, leaves, fruit.
Abilities = can/can't: jump, eat, drink, walk, run, climb, swim, dive, talk, sing. LIVE.
Adjetives: dangerous, funny, fast, slow, very colourful.
Vocabulario pasivo:
- Behavior: aquatic, domesticated, wild, endangered, extinct, hibernating, migratory, nocturnal, poisonous, social, solitary, terrestrial, territorial, venomous.
- Types: mammal, amphibian, bird, reptile, fish, insect.
Estructuras
Para hacer descripciones, generalmente usamos el sujeto THEY, porque describimos cómo son los animales en general (lo hacemos en plural). También por esta razón no usarmos el artículo THE delante del nombre de los animales, porque hablamos en general (decimos HIPPOS, en lugar de *THE HIPPOS*).
- DESCRIPTION:
- size (big, small, medium)
- colour
- body parts (tail, horns, wings...)
- behavior (funny, dangerous, strong, fast...)
Ejemplos:
- Lions are big cats.
- Monkeys are brown and funny.
- Rhinos have got one or two horns.
Frases sencillas para practicar size/colour/body parts.
- DIET: Usamos el verbo EAT, junto con un
sustantivo relacionado con la comida (grass, leaves, small animals,
fruit...). Según lo que comen, podemos clasificar los animales como:
- HERBIVORES
- CARNIVORES.
- Lions eat death animals.(They like eating zebra's meat).
- Lions are carnivores.
- HABITAT: Usamos el verbo LIVE, junto algunos
sustantivos o complementos del lugar (on, land, in water, in the
mountains, forest, jungle, desert, ocean...). Según donde, podemos
clasificar los animales como:
- terrestial (they live on land).
- aquatic (they live in water).
- Lions live in Africa, in the savannah.
- They are terrestial, because they live on land.
- TYPES: Usamos el verbo to BE para describir los tipos de animales (mammal, reptile, bird...).
Ejemplo:
- Lions are terrestial mammals.
- ABILITIES: Usamos el verbo CAN (o en su forma negativa, CAN'T), junto con un verbo (fly, jump, run, swim, talk, climb, dive, crawl).
Ejemplo:
- Lions can run and jump, but they can't dive.
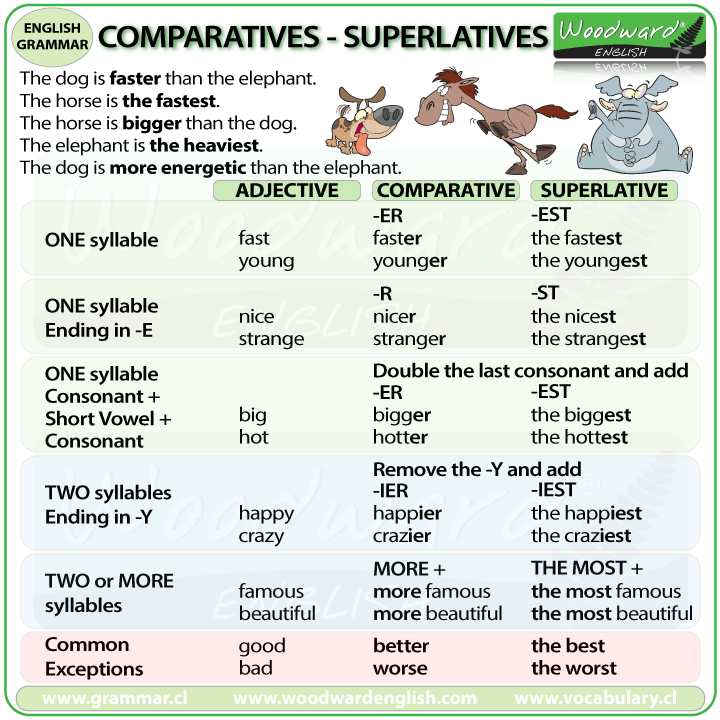
COMPARATIVES AND SUPERLATIVES
We use Comparatives and Superlatives to compare two or more nouns.
The formation of the comparative and superlative depends on the number of syllables in the adjective:
One-syllable Adjectives
To form the comparative, we add -er to the end of the adjective.
To form the superlative, we add -est to the end of the adjective.
| Adjective | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| small | smaller | the smallest |
| cold | colder | the coldest |
| light | lighter | the lightest |
| wide * | wider | the widest |
| hot ** | hotter | the hottest |
* When an adjective ends in the letter E, we just add the -R (for comparatives) or -ST (for superlatives). We do not write two Es together. Wider (correct) not wideer (incorrect).
** When an adjective ends in a consonant + short vowel + consonant (C + V + C), we normally double the last letter. big - bigger - biggest, wet - wetter - wettest
- London is bigger than Santiago.
- Mike is taller than John but James is the tallest.
- Yesterday was the hottest day of the year.
- It is the oldest building in the village.
- I want a faster car.
Notice how comparatives are often followed by than when comparing two things or people.
Two-syllable Adjectives ending in -Y
To form the comparative, we remove the -y and add -ier to the end of the adjective.
To form the superlative, we remove the -y and add -iest to the end of the adjective.
| Adjective | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| crazy | crazier | the craziest |
| happy | happier | the happiest |
| early | earlier | the earliest |
- It was the happiest day of my life.
- My joke was funnier than your one.
- This section is easier than the rest.
Adjectives with Two or more Syllables
For Adjectives with 2 syllables (that don't end in -y) and higher (3, 4 syllables etc), we use more for comparatives and the most for superlatives.
| Adjective | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| handsome | more handsome | the most handsome |
| nervous | more nervous | the most nervous |
| enthusiastic | more enthusiastic | the most enthusiastic |
- My girlfriend is more beautiful than yours.
- Alex is more intelligent than you but I am the most intelligent.
- It was the most wonderful day I have ever had.
Some exceptions with two-syllable adjectives ending in -er and -est:
narrow - narrower, simple - simpler, quiet - quieter
Irregular Forms
| Adjective | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| good | better | the best |
| bad | worse | the worst |
| far *** | further / farther | the furthest / farthest |
| little | less | the least |
| many/much | more | the most |
| old **** | older/elder | the oldest / eldest |
- I am a better tennis player than you but Marcelo is the best.
- Steve is a worse liar than me but Adrian is the worst.
*** Farther - Further
Further / farther, furthest / farthest are all used for distance.
Only Further / furthest are used to mean 'additional' or 'more advanced'.
- Puerto Montt is further / farther than Valdivia is from here (in Santiago).
- If you require further information, please contact reception.
Remember that the opposites of 'more' and 'most' are 'less' and 'least', respectively.
**** Older - Eldest
We use elder / eldest when we are talking about family relationships and normally only before a noun (not by itself unless it is a pronoun).
- He is my elder brother. (We cannot say: My brother is elder than me. - incorrect)
- The eldest sister would pass on her dresses to the younger one.
AT THE ZOO. Proyecto de investigación sobre animales . Crear un álbum de recortes sobre los animales trabajados . Cada uno buscará imágenes relacionadas con su animal, y redactará un pequeño texto descriptivo: dónde viven, qué comen, de qué color son, si tienen pelo/plumas/piel, alas/patas/cola, y lo que puede o no pueden hacer (correr, volar, saltar, hablar, arrastrarse, andar...).
Actividades de Ampliación
Giant Pandas: Reading and Listening Comprehension. Un cuento popular sobre cómo los pandas adquieren su color y un interesante vídeo sobre pandas gigantes salvajes, para desarrollar destrezas de lectura y comprensión auditiva.
Koalas: No Tree .... No Me. Comprensión auditiva y lectura sobre koalas. Se puede usar con el imprimible ´Animals from Down Under" para practicar las cuatro destrezas.
The Mosquito: Listening and Reading Comprehension. Un interesante vídeo de National Geographic sobre el animal favorito de nadie, el mosquito, para practicar la comprensión auditiva, y un texto sobre cómo evitar los picotazos de mosquitos, para leer.
Study “there’s / there are” and “prepositions of place”
Police station
Sports centre
Museum
Bank
Theatre
Shopping centre
Restaurant
Cathedral
Between
Town centre
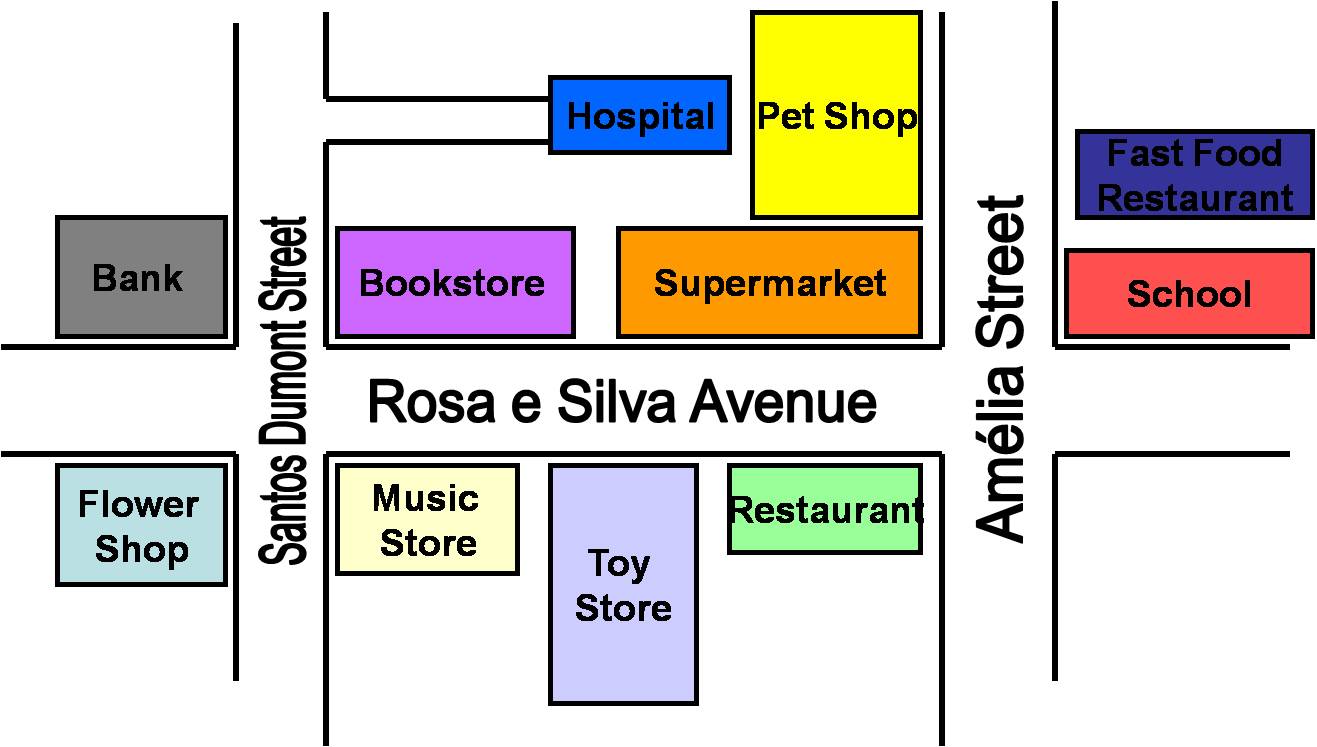
PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE I
Preposition of Place
Observe the map and choose the correct preposition.

1. The music store is Santos Dumont Street and Rosa e Silva Avenue.
2. The hospital is the pet shop.
3. The toy store is the music store and the restaurant.
4. The supermarket is the restaurant.
5. The fast food restaurant is Amélia Street.
6. The bookstore is the supermarket.
7. The school is Amélia Street and Rosa e Silva Avanue.
9. The pet shop is Amélia Street.
10. The flower shop is Santos Dumont Stree.
Cinema
Toy shop
Park
Behind
Next to
Opposite
Turn left
Go straight on
Turn right
She’s [jumping, running, walking, riding her bike, eating….]
He’s wearing [trousers]
EXERCISE 1
True and False. Observa la imagen y lee las frases. Marca TRUE (verdadero) o FALSE (falso).
EXAMPLE
1.Excuse me,how can I go to the _______________?
Walk along the Violet Street.Take the first turning on the right.Go straight on.It's on your left between
the restaurant and the hospital.
THE TREASURE MAP
I LIKE MY NEIGHBOURHOODEXERCISE 1
True and False. Observa la imagen y lee las frases. Marca TRUE (verdadero) o FALSE (falso).
| Language for asking directions | ||||
| Can you tell me Do you know |
the way to how to get to |
the | (nearest) | post office bus stop toilet |
| Covent Garden Trafalgar Square Bush House |
||||
| Language for giving directions | |
| Left go left turn left it's on the left take a left take the second (turning) on the left |
 |
| Right go right turn right it's on the right take a right take the second (turning) on the right |
 |
| Ahead go ahead go straight ahead go straight on |
 |
1.Excuse me,how can I go to the _______________?
Walk along the Violet Street.Take the first turning on the right.Go straight on.It's on your left between
the restaurant and the hospital.
GIVING DIRECTIONS
Verb to be. Past tense
| subject | main verb | |||
| + | I, he/she/it | was | here. | |
| You, we, they | were | in London. | ||
| - | I, he/she/it | was | not | there. |
| You, we, they | were | not | happy. | |
| ? | Was | I, he/she/it | right? | |
| Were | you, we, they | late? |
Verb To BE : Ser o estar
Present
I am: Yo soy
You are: Tú eres
He is: Él es
She is: Ella es
It is : Eso es
We are: Nosotros somos
You are: Vosotros sois
They are: Ellos son
Past
I was: Yo era
You were: Tú eras
He was: Él era
She was: Ella era
It was: Eso era
We were: Nosotros éramos
You were: Vosotros érais
They were: Ellos eran El verbo to be no necesita auxiliar. Para la interrogación cambia el orden y para la negación utiliza not.
TELLING THE TIME
Preguntar qué hora es
What time is it? It's twelve o'clock. Preguntar a qué hora sucede una acción
What time do you go to school? At quarter to nine. Preguntar a qué hora estábamos en un sitio. Example: What time were you at Times Square? We were at Times Square at six o'clock. Preguntar dónde estábamos a un hora. Example: Where was he at four o'clock? He was at home at four o'clock. Make sentences using this structure: Where + was/were + sujeto + at + time ? Sujeto + was/were + at + place + at + time ¿Dónde estuviste tú a las cuatro en punto? Yo estuve en casa a las cuatro en punto. ¿Dónde estuvo ella a las diez y media? Ella estuvo en el colegio a las diez y media. ¿Dónde estuvísteis vosotros a las dos y cuarto? Nosotros estuvimos en el restaurante a las dos y cuarto. ¿Dónde estuvieron ellos a las siete menos cuarto? Ellos estuvieron en el centro comercial a las siete menos cuarto. |
Write the digital time.
Example:
12: 34 : It's twelve thirty four
UNIT 6
VOCABULARY
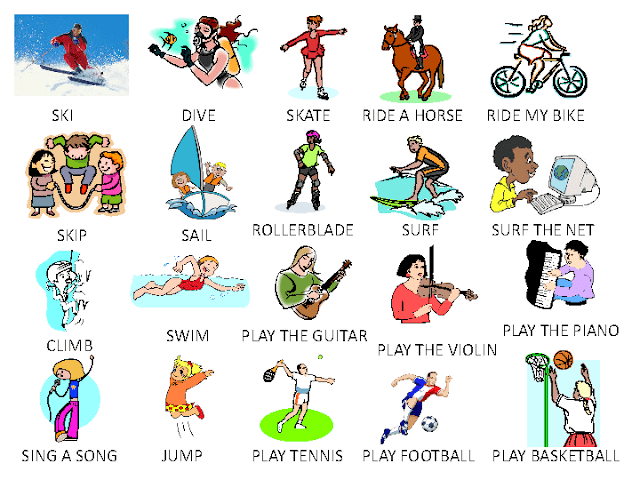
ACTIVITIES - VERBS: go snorkelling, go waterskiing, go surfing, go kayaking, go climbing, go hiking, go horseriding, go cycling
wind-surfing, rollerblading, sailing, go shopping, fishing, swimming, taking photos, cycling, walking, running, drinking, listening to music, eating, wearing, diving, riding a bike, flying a kite, reading.
- DAYS OF THE WEEK (repaso): Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday.
GRAMMAR
Want:
AFFIRMATIVE / NEGATIVE
SUJ = I, you, we, they ----> WANT / DON'T WANT TO GO +V-ing.
SUJ = he / she / it ---> WANTS / DOESN'T WANT TO GO +V-ing.
INTERROGATIVE
SUJ= DO------ I, you, we, they------WANT TO GO +V-ing?
SUJ= DOES ---he/she/it--------------WANT TO GO +V-ing?
Ej.:
The boy doesn't want to go skateboarding in the park.
Does the boy want to go skateboarding in the park?
RESPUESTA BREVE
-- Yes, SUJ (pronombre) + AUX
-- No, SUJ (pronombre) + AUX NEG
Ej.:
-- Yes, he/she/it does.
-- No, he/she/it doesn't.
--Yes, I/you/we/they do.
-- No, I,you/we/they don't
ON + DÍA DE LA SEMANA = los... (lunes)
Se puede poner tanto al principio (más una coma) como al final de la frase.
Ej.:
On Monday, I want to go shopping.
I want to go shopping on Monday.
SENTENCES. Translate.
Example:
Mary quiere ir a practicar escalada. Mary wants to go climbing.
Yo quiero ir a hacer submarinismo.
Él quiere hacer piragüismo el sábado.
Nosotros queremos montar a caballo el domingo.
Example
Yo no quiero hacer surf el martes. I don't want to go surfing on Tuesday.
Ella no quiere ir a hacer senderismo el jueves.
Beth no quiere ir a navegar el lunes.
Tom quiere hacer escalada pero no quiere hacer senderismo.
Example:
¿Quieres tú ir a practicar esquí acuático? No. Do you want to go water-skiing? No, I dont.
¿Quiere él hacer ciclismo el lunes? Si.
¿Quieren ellos ir a montar a caballo el viernes? No.
¿Quiere Tom ir a patinar el miércoles? Si.
- SUJ + WANT TO + V
- SUJ + WANT TO GO + V-ing
AFFIRMATIVE / NEGATIVE
SUJ = I, you, we, they ----> WANT / DON'T WANT TO GO +V-ing.
SUJ = he / she / it ---> WANTS / DOESN'T WANT TO GO +V-ing.
INTERROGATIVE
SUJ= DO------ I, you, we, they------WANT TO GO +V-ing?
SUJ= DOES ---he/she/it--------------WANT TO GO +V-ing?
Ej.:
The boy doesn't want to go skateboarding in the park.
Does the boy want to go skateboarding in the park?
RESPUESTA BREVE
-- Yes, SUJ (pronombre) + AUX
-- No, SUJ (pronombre) + AUX NEG
Ej.:
-- Yes, he/she/it does.
-- No, he/she/it doesn't.
--Yes, I/you/we/they do.
-- No, I,you/we/they don't
ON + DÍA DE LA SEMANA = los... (lunes)
Se puede poner tanto al principio (más una coma) como al final de la frase.
Ej.:
On Monday, I want to go shopping.
I want to go shopping on Monday.
SENTENCES. Translate.
Example:
Mary quiere ir a practicar escalada. Mary wants to go climbing.
Yo quiero ir a hacer submarinismo.
Él quiere hacer piragüismo el sábado.
Nosotros queremos montar a caballo el domingo.
Example
Yo no quiero hacer surf el martes. I don't want to go surfing on Tuesday.
Ella no quiere ir a hacer senderismo el jueves.
Beth no quiere ir a navegar el lunes.
Tom quiere hacer escalada pero no quiere hacer senderismo.
Example:
¿Quieres tú ir a practicar esquí acuático? No. Do you want to go water-skiing? No, I dont.
¿Quiere él hacer ciclismo el lunes? Si.
¿Quieren ellos ir a montar a caballo el viernes? No.
¿Quiere Tom ir a patinar el miércoles? Si.
Cornwall
5- Where is Cornwall?
6- What's the weather like in summer?
7- What activities can you do in Cornwall?
8- What is the best activity?
OUTDOOR ACTIVITIES
OUTDOOR ACTIVITIES
INTERACTIVE BOOK ( PAST TENSE )
PASADO - Simple Past
| Tiempo | Oraciones | Usos | Indicadores |
| Simple Pastxx | A: He lived here. N: He didn't live here.xx Q: Did he live here? | • Acción en el pasado, que se desarrolló una vez, varias veces o nunca.xx • Acciones que tuvieron lugar una detras de otra. • Acción que tuvo lugar en medio de otra. | • yesterday • 2 minutes agoxx • in 1990 • the other day • last Friday |
Cómo se forma el verbo en pasado
| to BE | to HAVE | Verbos Regulares |
| I was you were he/she/it was we were you were they were | had (para todas las personas) | Añadiendo el sufijo -ed a la forma verbal Si el verbo termina en -y-, ésta cambia a -i- cuando se añade -ed. Por ejemplo: cry > cried. |
Estructura de la frase en pasado
En general, las oraciones en pasado tienen el mismo orden que las oraciones en presente:
- A.: SUJETO + VERBO + COMPLEMENTO.
- N.: SUJETO + AUXILIAR + N'T + COMPLEMENTO.
- Q.: AUXILIAR + SUJETO + VERBO + COMPLEMENTO?
Por tanto, lo único que varía es el AUXILIAR que se va a utilizar.
Auxiliares: DID - WAS / WERE -
- Los verbos to BE y to HAVE son verbos auxiliares y no necesitan otro auxiliar. Por tanto, si una frase lleva uno de estos verbos, el orden será:
- A.: SUJETO + VERBO AUX. + COMPLEMENTO.
- N.: SUJETO + VERBO AUX-N'T + COMPLEMENTO.
- Q.: VERBO AUX + SUJETO + COMPLEMENTO?
|
- El resto de verbos, necesitan un auxiliar, que en pasado es DID. Cuando se incluye el auxiliar de pasado en la frase, el verbo deja de ir en pasado y se adopta su forma de presente. Si una frase lleva uno de estos verbos, el orden será:>> A.: SUJETO + VERBO + COMPLEMENTO.
- N.: SUJETO + AUX-N'T + VERBO + COMPLEMENTO.
- Q.: AUX + SUJETO + VERBO + COMPLEMENTO?
|
|
- TRANSLATE THE SENTENCES ( BE/HAVE)
- TRANSLATE THE SENTENCES ( REGULAR)
Unit 4 - A school in China
Subjects
English Inglés
Science / History Conocimiento del Medio
Maths Matemáticas
Art Plástica
Chinese Chino
Sport - Phisycal Educaction Deportes o Educación física
Music Música
Language Lengua
Religion Religión
Citizenship Ciudadanía
Places at School
Classroom Clase
Gym Gimnasio
Lab Laboratorio
Playground Recreo
Music classroom Clase de música
Canteen Comedor
Toilets Servicios
Hall Entrada
Assembly hall Salón de actos
Staffroom Sala de profesores
Office Despacho
Porch Porche
Track Pista
Schoolyard Patio
Ramp Rampa
Food
(repaso): ice cream, sandwiches, apples, cheese, salad, pizza, biscuits, cherries, chocolate, cake, fish, melon, bananas, pork, yoghourt, milkshake, orange juice, rice, chicken, watermelon, tomatoes, milk, chips, vegetables, soup...
Meals of the day
breakfast desayuno
lunch almuerzo
dinner cena
STRUCTURES:
Where do you / they have (English)? ¿Dónde tienes/tienen Inglés?
I/they have (English) in clasroom 5 Yo tengo/ellos tienen Inglés en la clase 5.
Where does he/she have (Sport)? ¿Dónde tiene él/ella deporte?
He/she has sport in the (gym). Él/ella tiene deporte en el gimnasio..
When do you/they have (Music)? I/they have music on (Mondays and Wednesdays). ¿Cuándo tienes/tienen música? Yo tengo/ellos tienen música los lunes y los míercoles
When does he/she have (Chinese)? He/she has (Chinese) on (Tuesdays and Thursdays). ¿Cuándo tiene él/ella chino? Él/ella tiene chino los martes y jueves.
What do you have for (breakfast)? ¿Qué tomas para desayunar?
I have (fruit) for breakfast. Yo tomo fruta para desayunar
What does he/she have for (lunch)? ¿Qué toma él/ella para almorzar?
He/she has (pasta) for (lunch). Él/ella toma pasta para almorzar
Make your timetable in English on a sheet or a small cardboard, then, write a sentence with every subjet . Example, I have Music on Tuesdays. You must write the subjects and the days of the week always with capital letters. -->
Historia ( Listen and read )
Answer the questions: Where does he have English?
Does he like English?
Do you like English? Why/ Why not?
What is his favourite sport?
What is your favourite sport?
Can Beth and Tom jump and kick?
Reinforce Activities
- Do and does
- Subjects
- School subjects
- Shool subjects
- School subjects
- Hangman
- Present simple
- To have
- To have present
- To have present
- Food difficult
- Food easy
- Food intermediate
FOOD
DRINKS
VEGETABLES
FRUIT
BREAKFAST
JUNK FOOD
The very hungry caterpillar ( story )
Healthy food
Word - search
A RECIPE
EASY FRENCH TOAST
INGREDIENTS
TWO EGGS
¼ CUP MILK
1 TEASPOON CINNAMON
½ TEASPOON VANILLA ESSENCE OR EXTRACT.
4-6 SLICES THICK BREAD.
PREPARATION
MIX EGGS, MILK, CINNAMON AND VANILLA IN A BOWL.
HEAT A NON- STICK FRY PAN.
DIP BREAD IN EGG MIXTURE ON EACH SIDE. COOK , TURNING AFTER A MINUTE OR WHEN LIGHTLY BROWNED.
SERVE WITH CINNAMON, SUGAR, JAM, FRUIT OR TOPPING OF CHOICE.
UNIT 5 A DAY IN CANADA
LISTEN TO THIS TRADITIONAL SONG
VOCABULARY ( DAILY ROUTINES)
I..... wake up, get up, get dressed, have breakfast, wash my face, brush my teeth, comb my hair, make my bed, go to school ( by bus, on foot....)/ start school, go home/finish school, have lunch, do my homework, play ( computer, friends...), feed my pet, have a shower, have dinner, wash the dishes ( housework), watch television, read a book and go to bed.
TIME
Para preguntar a qué hora se hace algo habitualmente se añade What time delante de Do o Does, para responder se empieza con At. Si lo que me pregunta es qué hora es en este momente se empieza con It is.
What time do you do your homework? At five o'clock.
What time is it? It is half past four.
Present simple Se usa para expresar nuestras rutinas diarias.
Forma afirmativa.
Se
forma con el pronombre + el verbo (I read: Yo leo), la forma verbal
nunca cambia, excepto en la 3º persona del singular (He, She, It).
Ésto suele suponer una dificultad, hay que acordarse de añadir una s (She reads: Elle lee).
A veces en vez de añadir s , se añade:
- es (wash - washes), cuando el verbo termina en sh.
- es (go - goes), también se añade cuando termina en o.
- ies (study - studies), cuando el verbo termina en y precedida de consonante.
Cuando el verbo es compuesto sólo se añade la s a la primera parte (gets up).
Para forma la forma interrogativa se
añade delante del pronombre Do siempre, excepto para la 3º persona del
singular (He,She It), que se le añade Does, y entonces no se le pone la
s.
Do you read? : ¿Lees tú? Does he read? : ¿Lee él?
Para la forma negativa. se coloca
Don't (contracción de Do not) entre el pronombre y el verbo. En la 3º
persona del singular (He, She, It) se cambia por Doesn't (contracción de
Does not) y tampoco se le pone la s. I don't read: Yo no leo.
She doesn't read: Ella no lee.
It se usa para animales, objetos, para hablar del tiempo, de la hora o de cosas abstractas.
Reinforce Activities
- Daily rutines – present simple
- Daily rutines exercise
- Every day activities
- Every day life
- Telling the time
- The time exercices
- Times exercice
- Times game
- Times game
- Times game
- What time is it?
- What's the time?
- What's the time?
- Habits & Routines. By Isabel Pérez.
PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE
ACTIVITY TO REINFORCE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE 1º AND 3º PERSON
THE WEATHER
Whatś the weather like ( today)?It's...
Reading
Read page 48 and aswer the questions.
Robert
1- How old is he?
2- Where does he live?
3- What's the weather like there?
4- What time does he get up?
5- What time does he do his homework?
6- What time does he go to bed?
Laura
7- How old is Laura?
8- Where does she live?
9- What's the weather like there?
10- What time does she get up in the week?
11- What time does she go to school?
12- What time does she have dinner?
REVIEW UNIT 5
DAILY ROUTINE
UNIT 6 ( PEOPLE OF NEW YORK)
VOCABULARY
Jobs
a
film star: estrella del cine
a
firefighter: bombero
a
baseball player: jugador de beisbol
a
nurse: enfermera/o
a
taxi driver: taxista
a
cook: cocinero/a
an
artist: artista
a
musician: músico/a
a
teacher: maestro/a
a
clown : payaso
a
doctor: doctor/a
a
farmer. granjero/a
a
baker: panadero/a
a
singer: cantante
Hay que colocar el artículo a/an delante de las profesiones.
Verb
To BE : Ser o estar
I
am: Yo soy o estoy
You
are: Tú eres o estás
He
is: Él es o está
She
is: Ella es o está
It is : Eso es o está
We
are: Nosotros somos o estamos
You
are: Vosotros sois o estáis
They
are: Ellos son o están
Past
I was: Yo era o estaba
You were: Tú eras o estabas
He was: Él era o estaba
She was: Ella era o estaba
It was: Eso era o estaba
We were: Nosotros éramos o estábamos
You were: Vosotros érais o estábais
They were: Ellos eran o estabanTO BE ( PAST TENSE)
PAST SIMPLE OF " TO BE "1
PAST SIMPLE OF " TO BE " 2
TO BE ( SIMPLE PRESENT/ SIMPLE PAST)
VOCABULARY( JOBS)
WELCOME TO NEW YORK
NEW YORK
Reading
Who is Tom Hanks?
Where is he from?
Has he got any awards?
Does he like football?
What’s his most famous role?
What’s his favourite singer?
Do you know more films by Tom Hanks?
Who is Ewan Macgregor?
Where is he from?
Where does he live?
Where is his wife from?
How many daughter has he got?
Was his mum a teacher?
What was his role in Star Wars?
Does he like singing and dancing?
What was his role in Moulin Rouge?
Do you know more films by Ewan Macgregor?




















Este comentario ha sido eliminado por un administrador del blog.
ResponderEliminarHola seno las actividades de tu blog son fáciles y divertidas gracias por todo
ResponderEliminarBay